Special Techniques & Molecular Pathology
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is a widely used method for detection of antigens (mainly proteins) in frozen or paraffin-embedded tissue sections. IHC exploits the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens. The histochemical demonstration of different enzymes or fluorescent dyes linked to antibody (e.g. peroxidase, alkaline phosphatase, FITC, Texas Red, etc.) serve as the detection system. At TPA, IHC is used for detection of proliferating cells, apoptotic cells, cell type markers, tumor markers, hormones and hormone receptors, oncoproteins, oncosupressor proteins, lymphoid markers, growth factors and their receptors, virus proteins, etc.
Kupffer cells in mouse liver (HIS36 IHC, frozen section). x80
01/24
IHC for Ovarian follicle counts
Enumerating ovarian follicles is an effective way to estimate the extent of ovarian toxicity in female rodents exposed to xenobiotics. Differential follicle counts are useful in safety assessment bioassays and in interspecies extrapolation of ovarian toxicity. Counting the follicles in H&E-stained sections is labor intensive, tedious, and costly. Here, at TPA, we demonstrated that in rat formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded ovary sections follicles of all degrees of maturity can be visualized by the use of antibody directed against proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). Follicles are easily distinguished from ovarian background with the ability to detect and identify primordial follicles being enhanced. This translates into a significant decrease in variability of follicle counts, labor, and cost.

PCNA-stained oocytes of primordial follicles in rat ovary (PCNA IHC). x160
IHC for Human in vitro air-liquid interface (ALI) models
ALI models create a fully differentiated, in vivo-like human bronchial epithelium. They provide a potential means to generate relevant data for evaluation cigarette smoke toxicity.

Proliferating cells in human ALI model (Ki67 IHC), x 160

Apoptotic bodies in human ALI model (Cleaved caspase-3 IHC), x160

Involucrin positive cells with signs of squamous differentiation in human ALI model (Involucrin IHC), x160
In Situ Hybridization
In situ hybridization (ISH) techniques allow detection of specific nucleic acid sequences in morphologically preserved cells or tissue sections. In combination with IHC, ISH can provide microscopic topological information about gene activity at the DNA, mRNA, and protein level.

Non-radioactive ISH for CYP1B1 mRNA, human brain. x40

Non-radioactive ISH for histone mRNA, mouse spleen. x100
Apoptosis Assays
Currently used apoptosis assays include Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase Mediated dUTP Nick End Labeling of DNA (TUNEL) and Caspase-3 immunohistochemistry. DNA fragmentation is a part of ultrastructural changes that are associated with apoptosis. In TUNEL assay, the DNA strand breaks are detected by enzymatically labeling the free 3’-OH termini with modified nucleotides.
Proliferation Assays
TPA currently uses proliferation assays that include Ki67, PCNA, BrdU IHC and In Situ Hybridization for Histone mRNA.
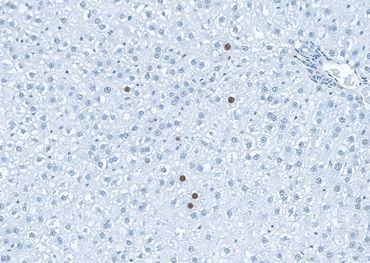
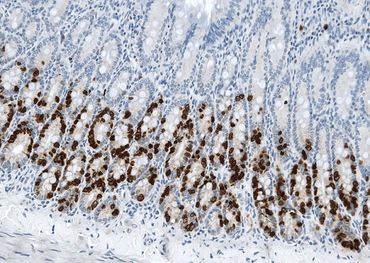
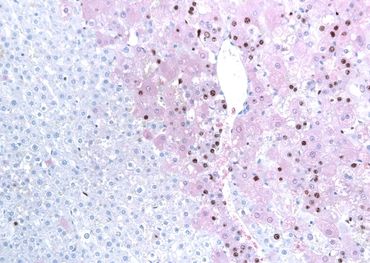

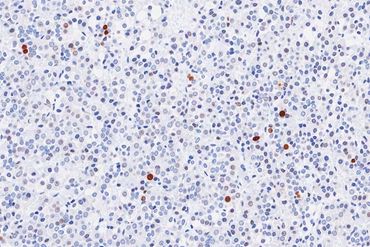
Image Analysis
IHC-stained sections are scanned and digital images are obtained by Aperio Scanscope System (Aperio Technologies, Inc., Vista, CA). In these images, intensity of staining, proportion of immunostained area and other parameters are evaluated with Positive Pixel Count Algorithm. This algorithm quantifies the amount of specific stain present in a digital image by evaluating average intensity of all pixels (Iavg); values of Iavg are then used to calculate optical density (OD). The Nuclear Algorithm evaluates numbers (%) of positively stained nuclei and quantifies the average staining intensity in individual cells.

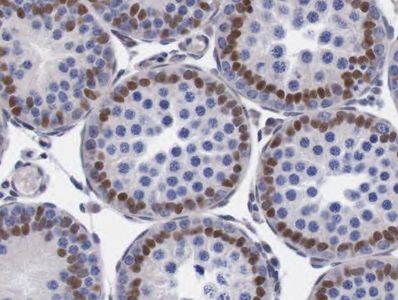
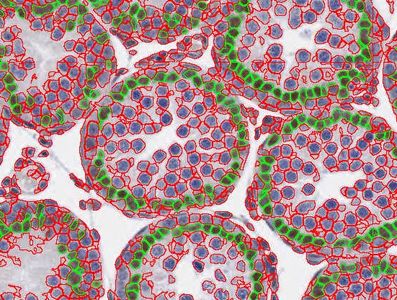
Automatic counting of Sertoli cell nuclei stained with Sox9. Rat testis. x80
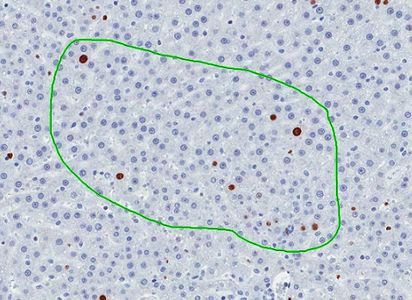
Automatic counting of proliferating cells in the outlined area of rat liver section (Ki67 IHC). x80
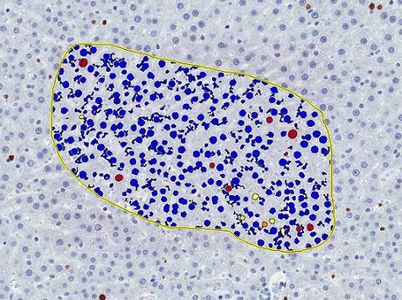
Automatic measurements of positively stained tissue and intensity of staining in the outlined area of GSTP-stained liver section. x4
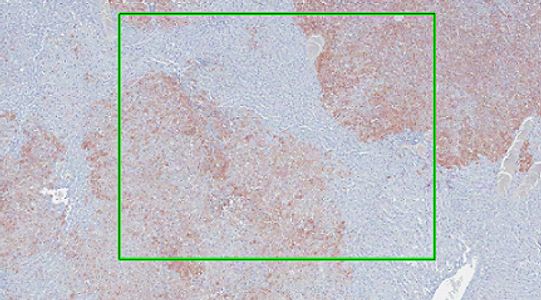
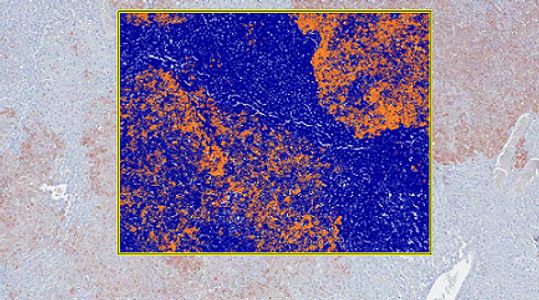
Automatic counting of proliferating cells in human ALI model (Ki67 IHC). x160


Automatic measurements of staining intensity and positively stained area (%) in human ALI model (CK13 IHC). x160


Automatic measurement of positively stained area (fat droplets) in the mouse liver (osmium tetroxide staining), x40


Organoids
Rat Testicular Organoids
Recently a 3D culture has been developed that allows the reorganization of rat primary testicular cells into organoids with a functioning blood-testis barrier, as well as the establishment and maintenance of germ cells. This technique is successfully used by NCTR investigators. TPA provides support for histological evaluation as well as immunohistochemical identification of types of cells and structures in the organoids.

Rat testicular organoid (H&E), x4

Proliferation in rat testicular organoid
(Ki67 IHC), x20

Blood-testis barrier in rat testicular organoid
(double staining with ZO-1 and DAPI), x60

Sertoli cells in rat testicular organoid
(Sox9 IF staining), x60